HTTP Cookies
Dr. Greg Bernstein
Updated October 19th, 2021
Cookies
Readings and Code
What? & Why? 1
From MDN
An HTTP cookie is a small piece of data that a server sends to the user’s web browser, the browser stores it and sends it back together with the next request to the same server.
Typically, it’s used to know if two requests came from the same browser allowing a user to stay “logged-in”. It remembers stateful information for the stateless HTTP protocol.
What? & Why? 2
From MDN
- Personalization (user preferences)
- Session management (user logins, shopping carts)
- Tracking (analyzing user behavior)
Security Caveats
There are a slew of important security and privacy issues related to cookies and their use. We will cover some of these in other slide sets.
How: Server Set’s Cookie
- In response message
- Use
Set-Cookie: <cookie-name>=<cookie-value> - With optional attributes
Set-Cookie: <cookie-name>=<cookie-value>; Path=/; Expires=datetime; ...
Example Response Message
From MDN
HTTP/1.0 200 OK
Content-type: text/html
Set-Cookie: yummy_cookie=choco
Set-Cookie: tasty_cookie=strawberry
[page content]Client action: return cookie
From MDN
with every new request to the server, the browser will send back all previously stored cookies to the server using the Cookie header.
Example Client Request
From MDN
GET /sample_page.html HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.org
Cookie: yummy_cookie=choco; tasty_cookie=strawberrySimple Preference Example
Bad Wind and Tide Predictor
cookieExample.mjs

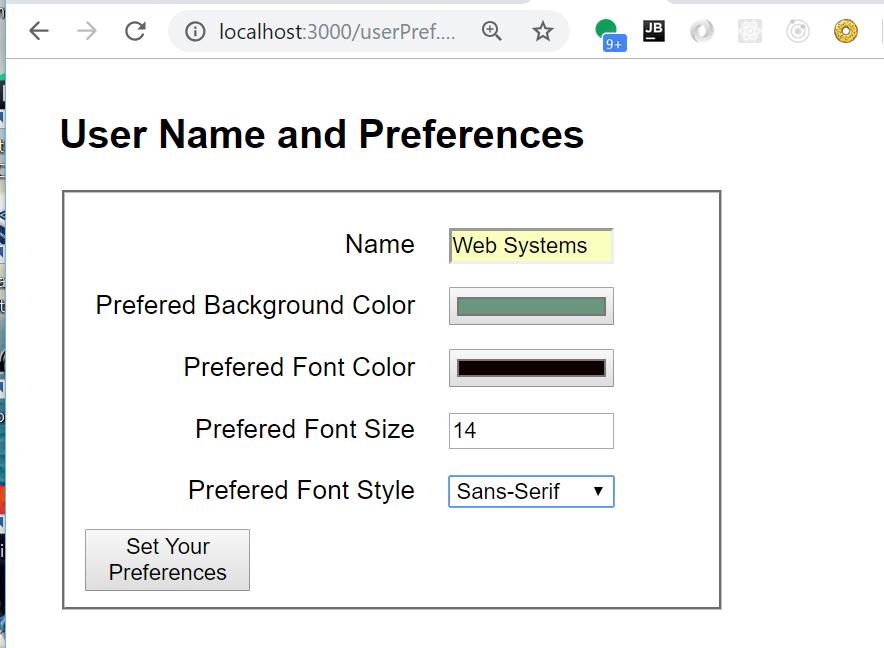
User Preference Form
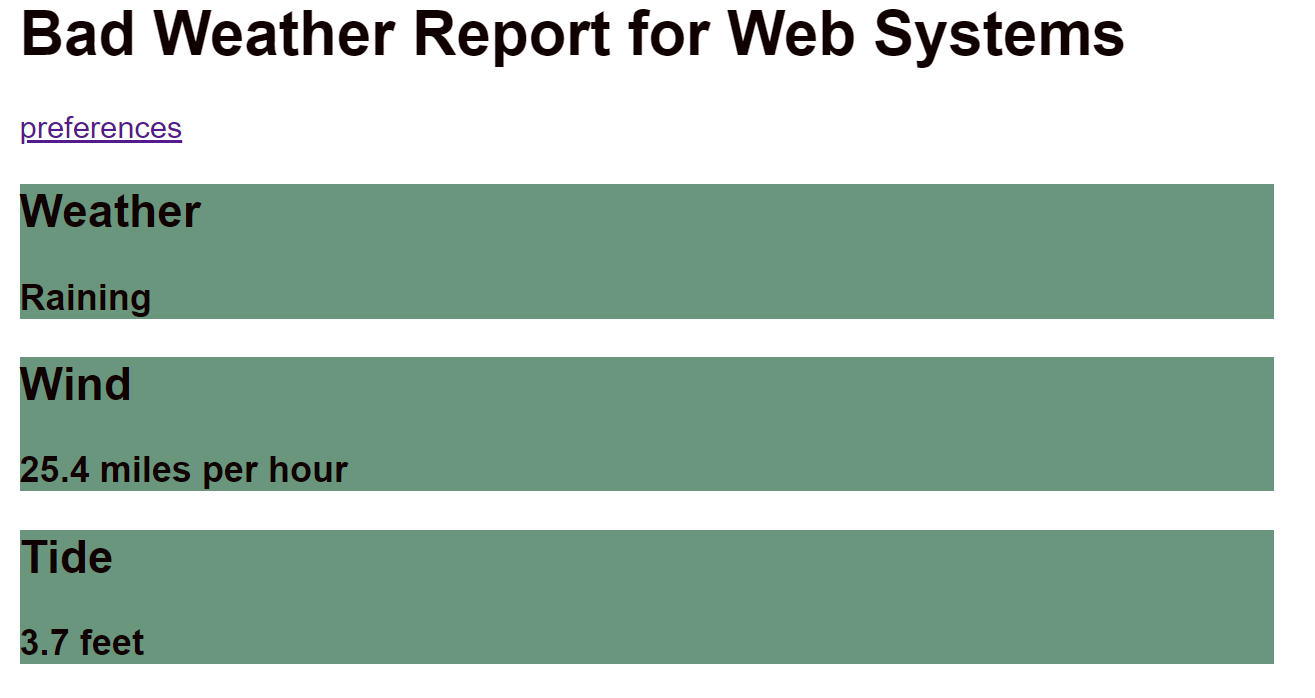
After Form Submission
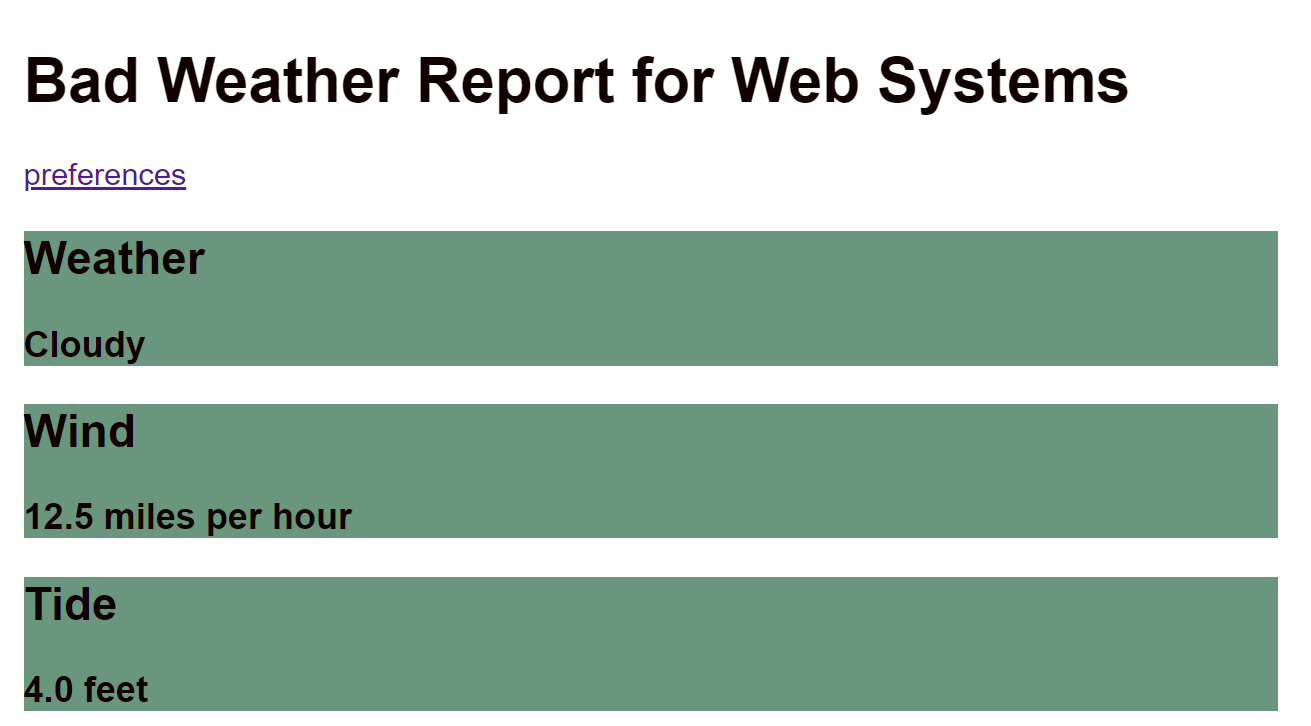
Close Tab and Reopen
How? A Cookie
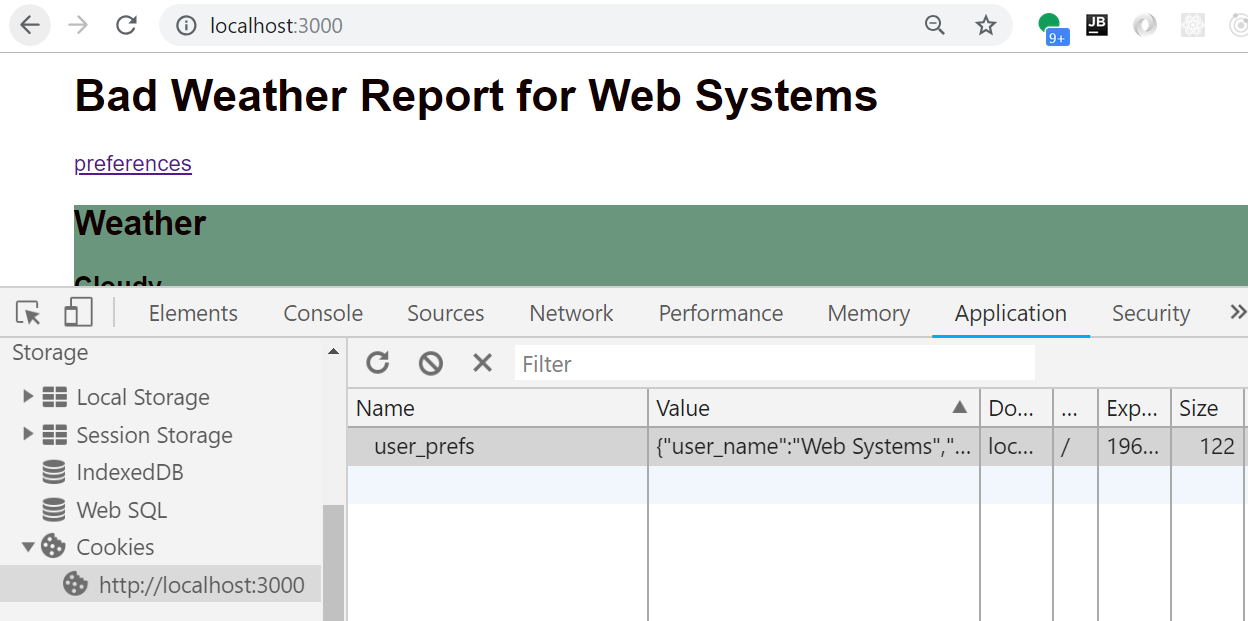
Network View 1
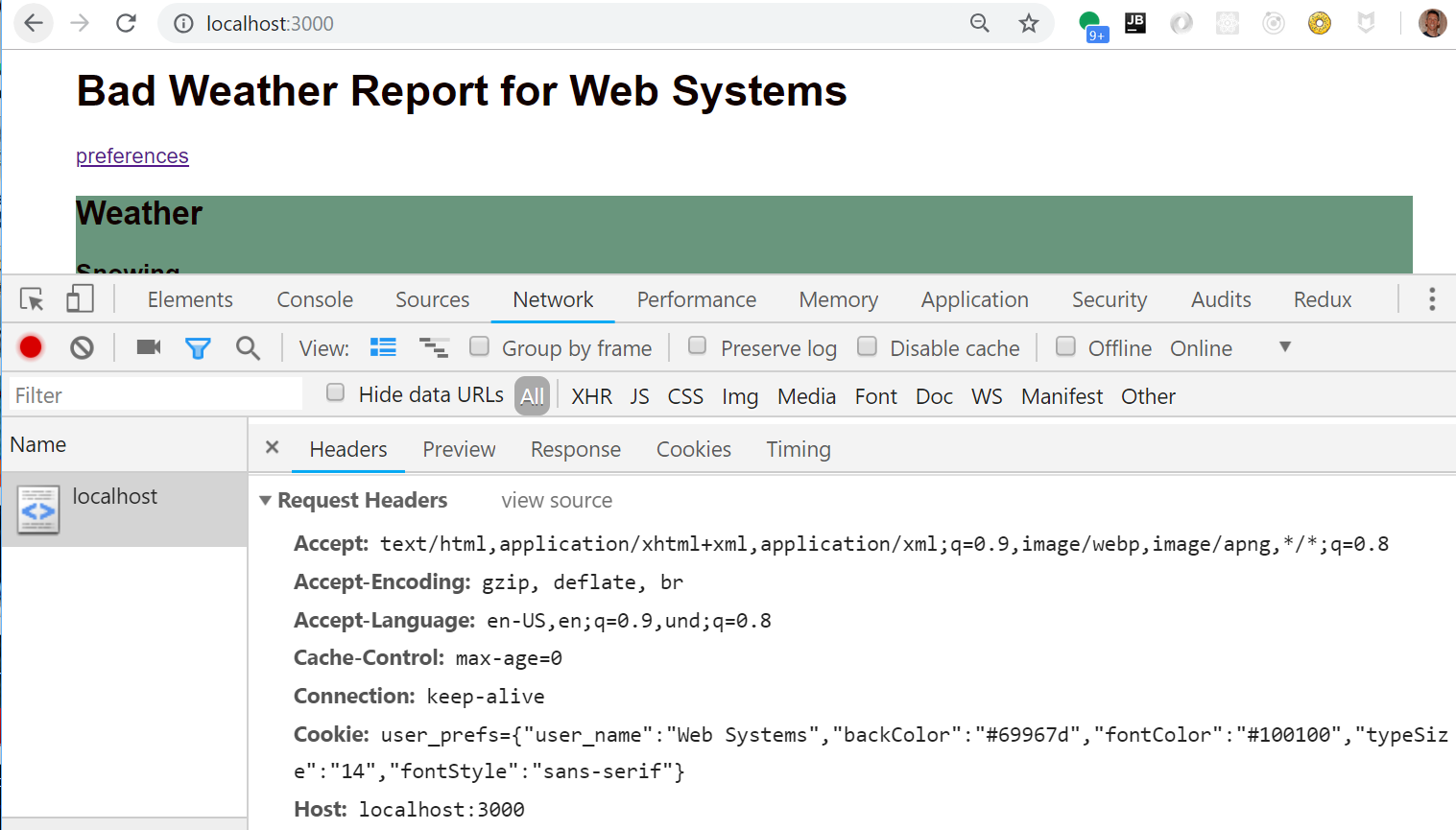
Processing The Cookie
From cookieExample.mjs get view:
import cookieParser from "cookie-parser"; // For cookies
app.use(cookieParser());
const weather = ["Sunny", "Cloudy", "Raining", "Broiling", "Snowing", "Partly Cloudy"];
const tideRange = [0.0, 6.0]; // In feet
const windRange = [0.0, 30.0]; // In MPH
const userPrefs = {user_name: "Our Friend", backColor: "#b6fcf4", fontColor: "#0000ff",
typeSize: "9", fontStyle: "serif"};
app.get("/", function(req, res) {
console.log("Cookies: ", req.cookies);
var prefs = userPrefs; // Default
if (req.cookies.user_prefs) { // Read back the preferences from the cookie
prefs = JSON.parse(req.cookies.user_prefs);
}
let info = {};
info.prefs = prefs;
info.weather = weather[Math.floor(Math.random() * Math.floor(weather.length))];
info.tide = (Math.random() * (tideRange[1] - tideRange[0]) + tideRange[0]).toFixed(1);
info.wind = (Math.random() * (windRange[1] - windRange[0]) + windRange[0]).toFixed(1);
res.render("weatherReport.html", info);
});Rendering the Weather
The weatherReport.html template
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Cookie Example</title>
<style>
main {
color: {{prefs.fontColor}};
font-size: {{prefs.typeSize}}pt;
font-family: {{prefs.fontStyle}};
margin: 2em;
padding: 1em;
}
.report {
background-color: {{prefs.backColor}};
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<main>
<h1>Bad Weather Report for {{prefs.user_name}}</h1>
<p><a href="userPref.html">preferences</a></p>
<section class="report">
<h2>Weather</h2>
<h3>{{ weather }}</h3>
</section>
<section class="report">
<h2>Wind</h2>
<h3>{{ wind }} miles per hour</h3>
</section>
<section class="report">
<h2>Tide</h2>
<h3>{{ tide }} feet</h3>
</section>
</main>
</body>
</html>Setting Preferences
From userPref.html
<form action="/setUserPrefs" method="post">
<fieldset>
<div class="formRow">
<label for="name">Name</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="user_name">
</div>
<div class="formRow">
<label for="backColor">Prefered Background Color</label>
<input type="color" id="backColor" name="backColor" value="#00FF00">
</div>
<div class="formRow">
<label for="fontColor">Prefered Font Color</label>
<input type="color" id="fontColor" name="fontColor" value="#100100">
</div>
<div class="formRow">
<label for="typeSize">Prefered Font Size</label>
<input type="number" id="typeSize" name="typeSize" value="16">
</div>
<div class="formRow">
<label for="fontStyle">Prefered Font Style</label>
<select name="fontStyle" id="fontStyle">
<option value="serif">Serif</option>
<option value="sans-serif">Sans-Serif</option>
<option value="monospace">Monospace</option>
<option value="cursive">Cursive</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="formRow">
<button type="submit">Set Your Preferences</button>
</div>
</fieldset>
</form>Processing The Form
From cookieExample.mjs:
// Respond to post request from form page.
app.post("/setUserPrefs", express.urlencoded({ extended: false }), function(req, res) {
/*console.log("Handling post request");
console.log("URL path:", req.path);
console.log("URL:", req.originalUrl);
console.log("Method", req.method); */
console.log("Body", req.body);
console.log("request HTTP version", req.httpVersion);
console.log("Content type", req.headers["content-type"]);
// Sets the cookie to a JSON string of user preferences. Two ways:
// res.append("Set-Cookie", "user_prefs=" + JSON.stringify(req.body));
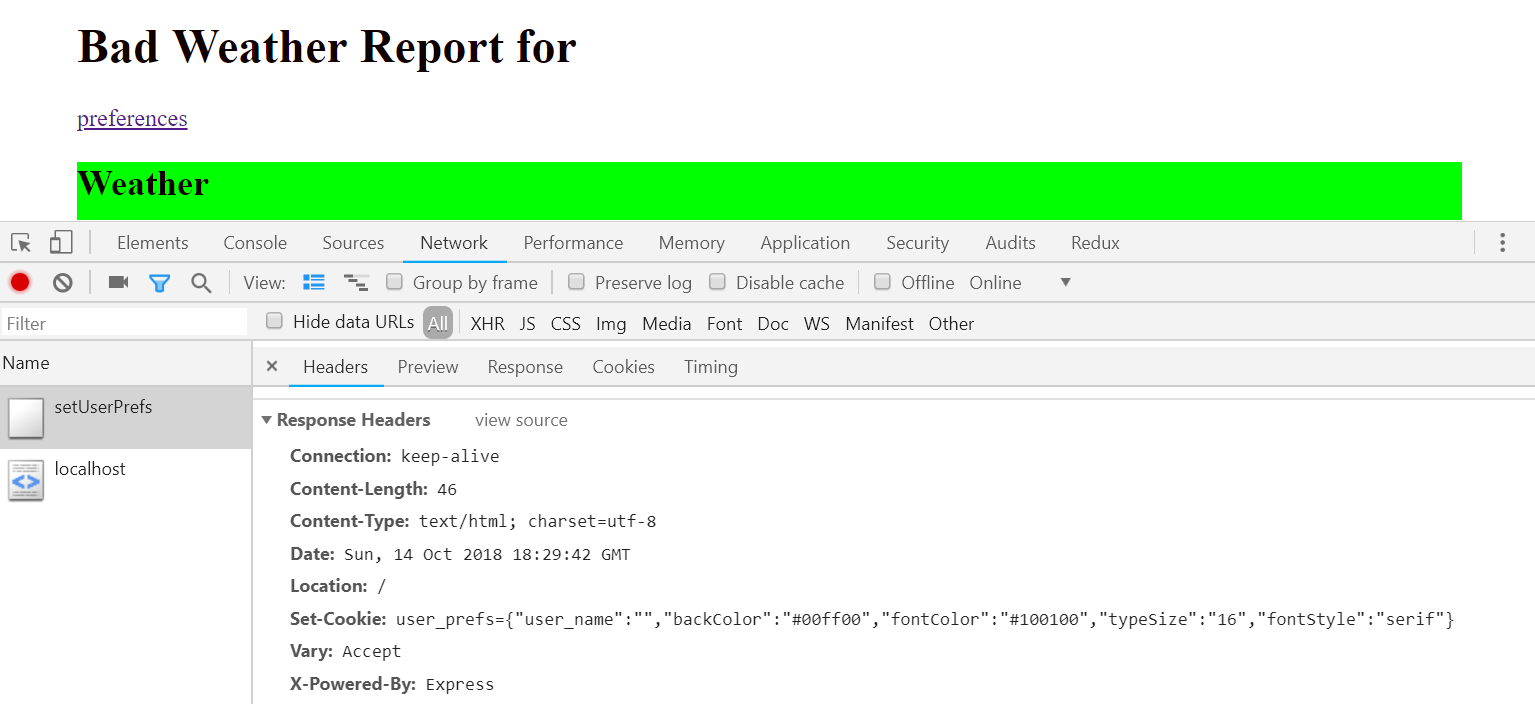
res.cookie("user_prefs", JSON.stringify(req.body));
res.redirect("/");
});Network View: Setting Cookie
Cookie Attributes
Cookie Duration
- Permanent Cookies
- Explicitly set
ExpiresorMax-Ageattributes Set-Cookie: id=a3fWa; Expires=Wed, 21 Oct 2015 07:28:00 GMT;
- Explicitly set
- Session Cookies
- “Expires when the browser is closed down”.
- Not really true anymore, most browsers have a “session restore” capabilities.
Try It
cookieExampleExt.mjs:
// Experiment with cookie options
const cookieOpts = {
// domain: "blah", // defaults to domain name
// expires: new Date() + 1000, // defaults to session cookie
httpOnly: false, // Browser JavaScript can't see it
maxAge: 5000, // Time from when it is set in ms, defaults to session cookie
path: "/", // default
secure: false, // Require HTTPS
signed: false, //
sameSite: "Lax"
};
// Respond to post request from form page.
app.post("/setUserPrefs", function(req, res) {
res.cookie("user_prefs", JSON.stringify(req.body), cookieOpts);
res.redirect("/");
});Who Can Receive the Cookie?
From MDN:
The
DomainandPathdirectives define the scope of the cookie, that is the set of URLs the cookies should be sent back to.
- Example:
Domain=grotto-networking.com; Path=/code/WebDev/Lectures;
Secure & HttpOnly
From Wikipedia: The Secure and HttpOnly attributes do not have associated values.
The
Secureattribute is meant to keep cookie communication limited to encrypted transmission, i.e., HTTPS, i.e., the browser will only send this cookie over HTTPS and not HTTP. Does not affect what the server does.The
HttpOnlyattribute directs browsers not to expose cookies through channels other than HTTP, i.e., the cookie is not available via JavaScript.
Same Site
From MDN:
SameSite cookies let servers require that a cookie shouldn’t be sent with cross-site requests, which somewhat protects against cross-site request forgery attacks (CSRF). SameSite cookies are still experimental and not yet supported by all browsers.