Intrusion Detection and Prevention
Dr. Greg Bernstein
May 2nd, 2022
System and Network Defense
References
- CyBOK Network Security (chapter 17): Network Defense Tools (section 17.8),
- CyBOK Security Operations (chapter 8): Architectural Principles (8.1.2), Monitor data sources (8.2), Analysis methods (8.3)
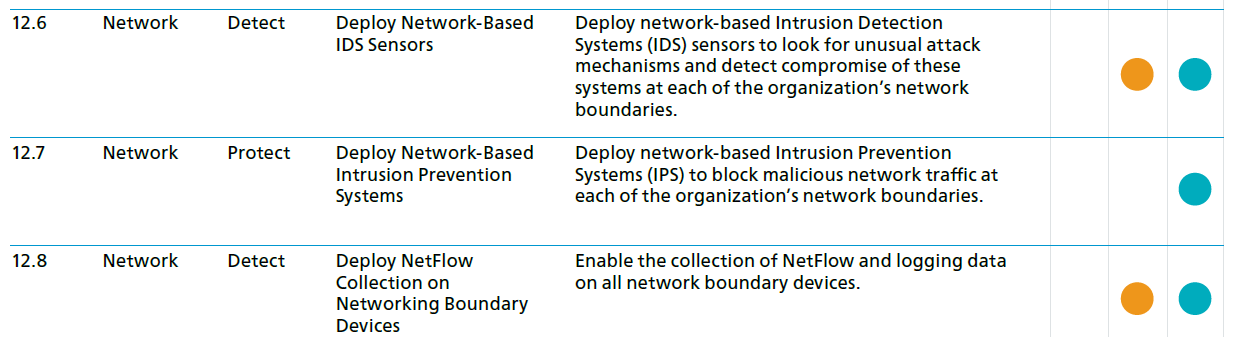
- CIS Control 12: Boundary Defense and CIS control PDF.
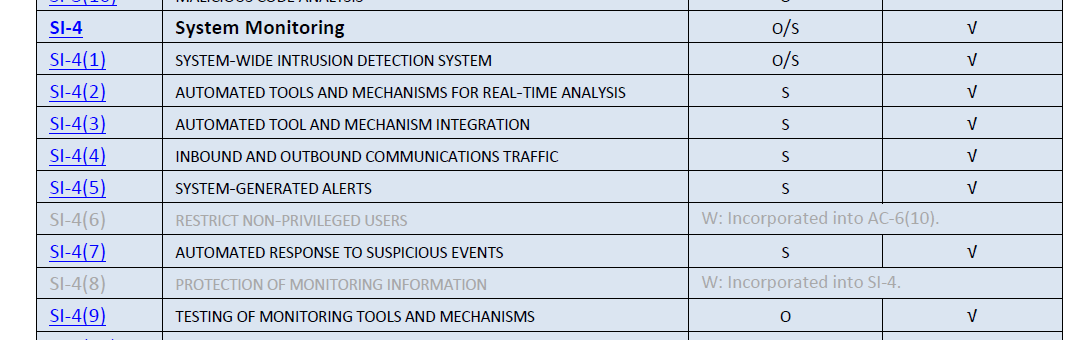
- NIST SP800-53: System Monitoring Control (SI-4)
System/Network Context
From CyBOK section 8.1.2
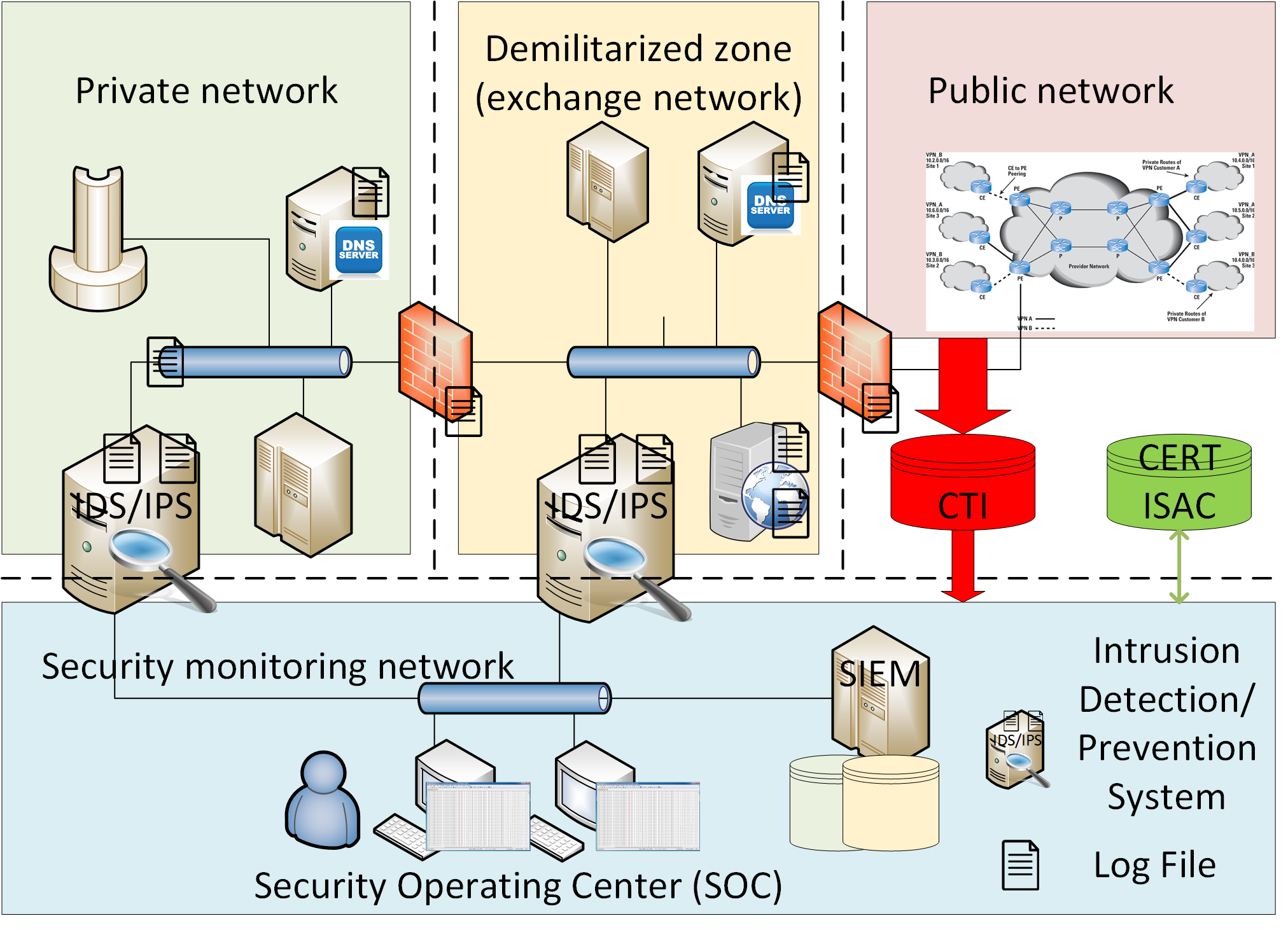
Key Components
- Public Network, e.g., the Internet
- Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
- Private Network
- Security Operating Center/Security Monitoring Network
DMZ Definition
From Wikipedia
In computer security, a DMZ or demilitarized zone is a physical or logical subnetwork that contains and exposes an organization’s external-facing services to an untrusted, usually larger, network such as the Internet. The purpose of a DMZ is to add an additional layer of security to an organization’s local area network (LAN): an external network node can access only what is exposed in the DMZ, while the rest of the organization’s network is fire walled.
DMZ Via Firewalls
From Wikipedia
Terminology
- SOIM: Security Operations and Incident Management, SOC: Security Operations (or Operating) Center
- SIEM: Security information and event management (system)
- CTI: Cyber Threat Intelligence, ISAC: Information Sharing and Analysis Center, CERT: Computer Emergency Response Team
Incident Response and Management: What
From CIS Control 19, organizational control
Protect the organization’s information, as well as its reputation, by developing and implementing an incident response infrastructure (e.g., plans, defined roles, training, communications, management oversight) for quickly discovering an attack and then effectively containing the damage, eradicating the attacker’s presence, and restoring the integrity of the network and systems.
Incident Response and Management: Why
From CIS Control 19, organizational control
Cyber incidents are now just part of our way of life. Even large, well-funded, and technically sophisticated enterprises struggle to keep up with the frequency and complexity of attacks. The question of a successful cyber-attack against an enterprise is not “if” but “when.”
When an incident occurs, it is too late to develop the right procedures, reporting, data collection, management responsibility, legal protocols, and communications strategy that will allow the enterprise to successfully understand, manage, and recover. Without an incident response plan, an organization may not discover an attack in the first place, or, if the attack is detected, the organization may not follow good procedures to contain damage, eradicate the attacker’s presence, and recover in a secure fashion.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
IDS: Definition
From Wikipedia: IDS
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a device or software application that monitors a network or system for malicious activity or policy violations. Any intrusion activity or violation is typically reported either to an administrator or collected centrally using a security information and event management (SIEM) system. A SIEM system combines outputs from multiple sources and uses alarm filtering techniques to distinguish malicious activity from false alarms.
IPS: Definition
From Wikipedia: IPS
Intrusion prevention systems (IPS) are network security appliances that monitor network or system activities for malicious activity. The main functions of intrusion prevention systems are to identify malicious activity, log information about this activity, report it and attempt to block or stop it.
Intrusion prevention systems are considered extensions of intrusion detection systems because they both monitor network traffic and/or system activities for malicious activity. The main differences are, unlike intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems are placed in-line and are able to actively prevent or block intrusions that are detected.
CIS Boundary Defense Controls
NIST Controls: System Monitoring
IDS/IPS Classification
From Wikipedia: IDS
Network-based intrusion detection/prevention system (NIDS/NIPS): monitors the entire network for suspicious traffic by analyzing protocol activity.
Wireless intrusion detection/prevention system (WIDS/WIPS): monitor a wireless network for suspicious traffic by analyzing wireless networking protocols.
Host-based intrusion detection/prevention system (HIDS/HIPS): monitors a single host for suspicious activity by analyzing events occurring within that host.
Detection Techniques
From Wikipedia: IDS
Signature-based detection: Signature-based IDS monitors packets in the Network and compares with pre-configured and pre-determined attack patterns known as signatures.
Anomaly-based detection: An IDS which is anomaly-based will monitor network traffic and compare it against an established baseline. The baseline will identify what is “normal” for that network – what sort of bandwidth is generally used and what protocols are used.
Open Source IDS/IPS
- Snort: NIDS, NIPS, rule based, no GUI
- Sucricata: NIDS, NIPS, rule based, GUI
- Zeek (formerly Bro): NIDS, rule and anomaly support, no GUI
- OSSEC: HIDS, multi-platform
- Fail2Ban: HIDS, with very specific functionality
Snort
From Snort 
“Snort is the foremost Open Source Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) in the world.” (according to them…)
Once downloaded and configured, Snort rules are distributed in two sets: The “Community Ruleset” and the “Snort Subscriber Ruleset.”, i.e., they make their money via subscriptions.
Suricata
- OS support: Linux, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, macOS, Windows
- Packet decoding: IPv4, IPv6, TCP, UDP, SCTP, ICMPv4, ICMPv6, GRE, Ethernet, PPP, PPPoE, Raw, SLL, VLAN, QINQ, MPLS, ERSPAN, VXLAN, Geneve
- App layer decoding: HTTP, HTTP/2, SSL, TLS, SMB, DCERPC, SMTP, FTP, SSH, DNS, Modbus, ENIP/CIP, DNP3, NFS, NTP, DHCP, TFTP, KRB5, IKEv2, SIP, SNMP, RDP, RFB, MQTT, New protocols developed in the Rust language, for safe and fast decoding.
Suricata at Home 1
- Want to watch all traffic for intrusions on a simple home network
- Cable Modem with separate home router/wireless access point
- Running OpenWrt on home router
Suricata at Home 2
- Set up Suricata on a Raspberry Pi
- Wired Ethernet Raspberry Pi to home router
- Enable port mirroring all incoming and out going traffic to Pi
Suricata at Home 3
Testing with a the site http://testmynids.org/uid/index.html
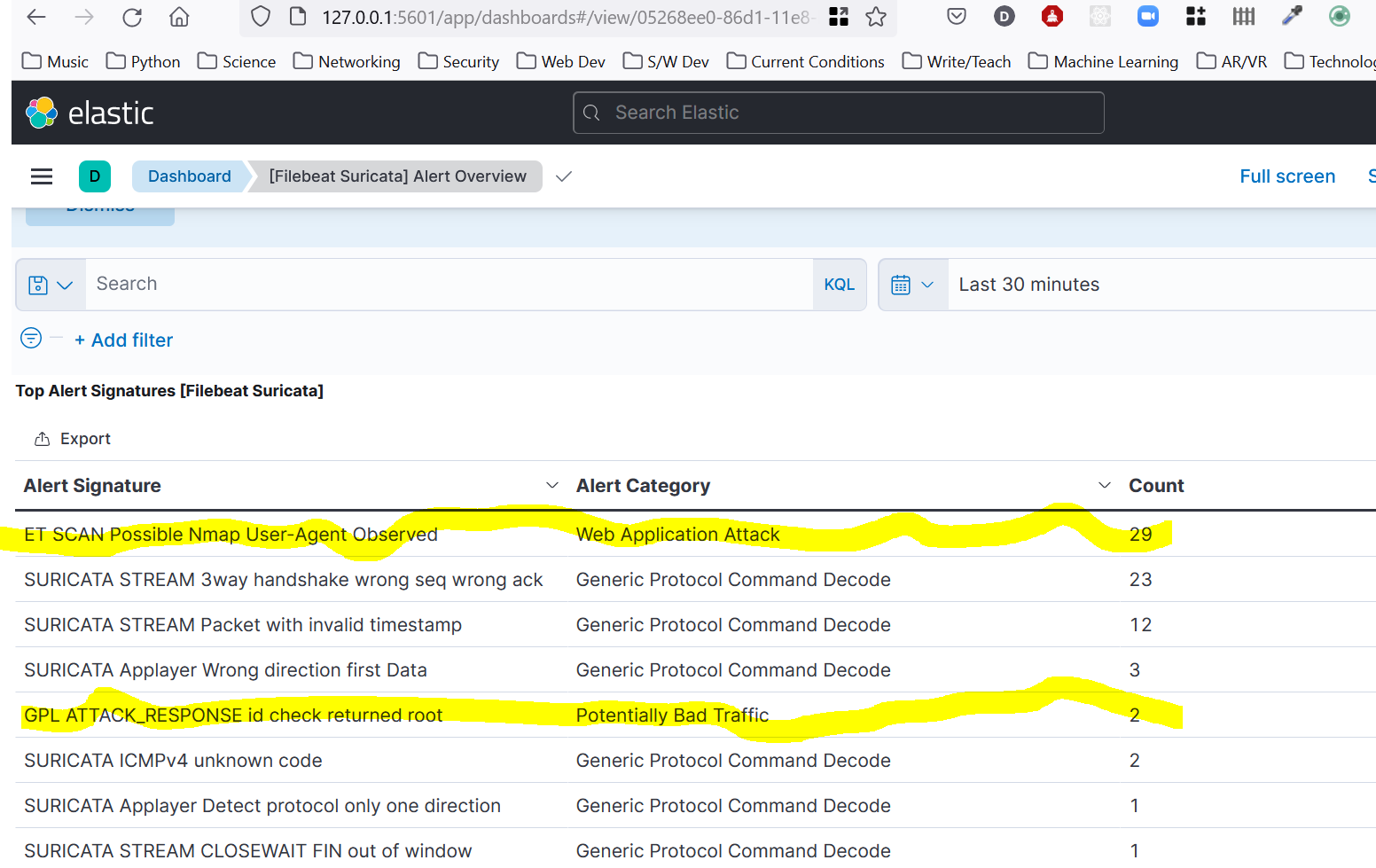
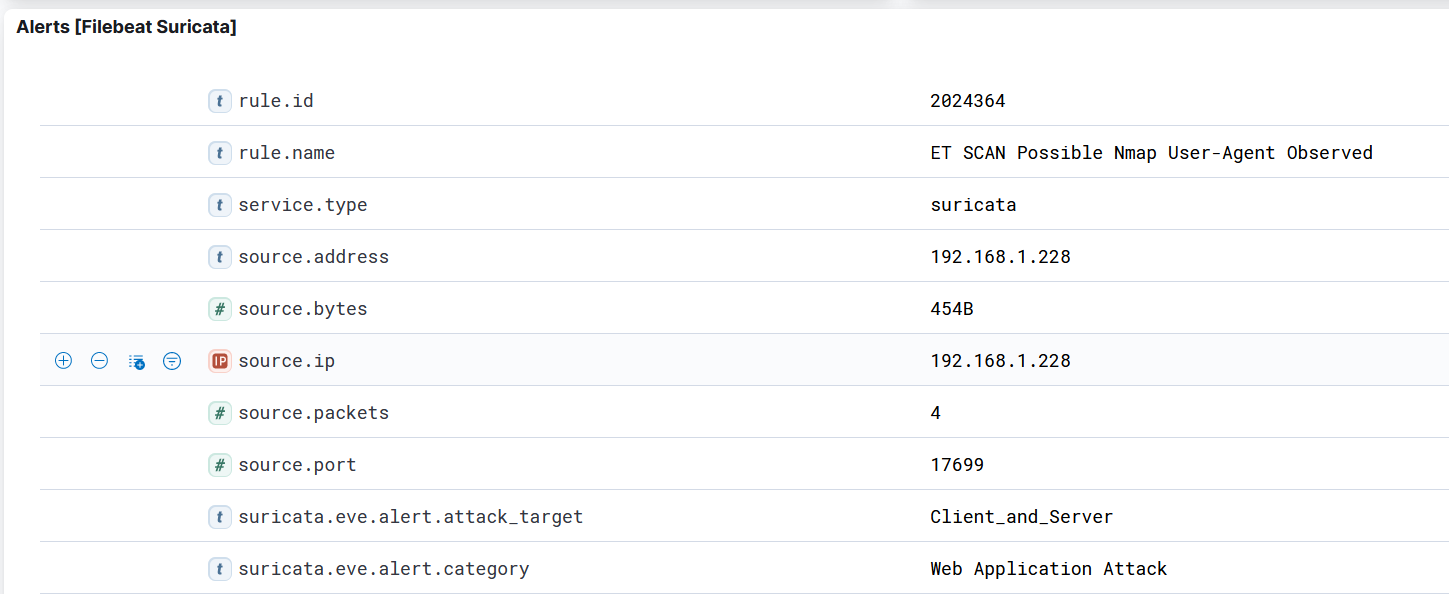
Suricata at Home 4
I ran an NMAP scan and it saw that too
OSSEC – Host Intrusion Detection
From OSSEC Home page 
OSSEC is a scalable, multi-platform, open source Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS)
Multiplatform HIDS: Linux, Solaris, AIX, HP-UX, BSD, Windows, Mac and VMware ESX.
PCI Compliance: OSSEC helps organizations meet specific compliance requirements such as PCI DSS. It detects and alerts on unauthorized file system modification and malicious behavior that could make you non-compliant.
Fail2Ban
From Wikipedia: Fail2Ban
Fail2Ban operates by monitoring log files for selected entries and running scripts based on them. Most commonly this is used to block selected IP addresses that may belong to hosts that are trying to breach the system’s security. It can ban any host IP address that makes too many login attempts or performs any other unwanted action within a time frame defined by the administrator. Includes support for both IPv4 and IPv6. Fail2Ban is typically set up to unban a blocked host within a certain period
