Physical Layers and Concepts
Dr. Greg Bernstein
January 29th, 2021
Wired Physical Layers
LAN (Local Area Network)
Ethernet now dominates the wired LAN infrastructure market. You will occasionally see mentions of older technologies such as token ring or specialized high performance computing technologies such as InfinBand, but these are extremely rare in most enterprises.
Ethernet References
- Wikipedia: Ethernet History and overview
- Wikipedia: Ethernet Frame
- Wikipedia: Ethernet Physical Layer Information about all the modulation formats, cables, and speeds
- Wikipedia: IEEE 802.3 List of all the various standards
Media Types, Speeds and Distances
Just a sample
- 100BASE‑TX (Fast Ethernet), Cat-5 twisted pair wire, 100 meters
- 1000BASE‑T (Gig Ethernet), Cat-5 twisted pair wire, 100 meters
- 10GBASE-SR, 10G over Multi-Mode fiber, 25-400 meters depending on fiber quality
- 40GbE, 100GbE over parallel multi mode fibers, over WDM single mode fibers. Single mode fibers can achieve distances up to 40km.
WAN: Optical Networks
See Optical slide set.
Advanced Concepts
Layers Again
Interoperability points: Physical and logical
Management: Fault isolation, Performance monitoring (where did the errors occur)
Multiplexing and Switching: Not just one switching layer!!!
Internet Protocol Layers
By en:User:Kbrose - Prior Wikipedia artwork by en:User:Cburnett, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1831900
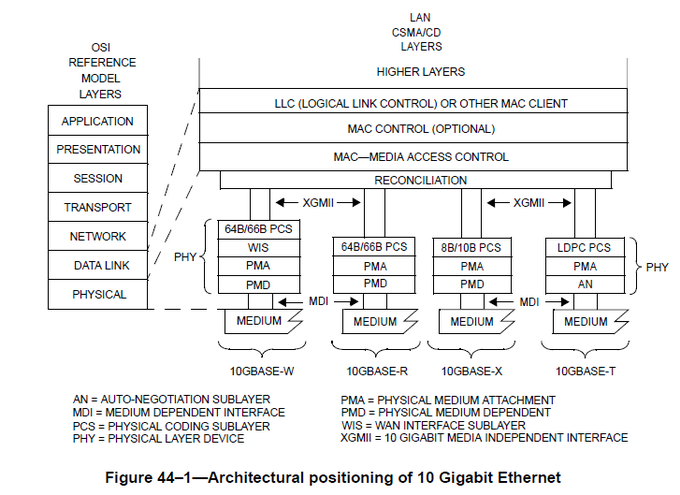
10G Ethernet Layers
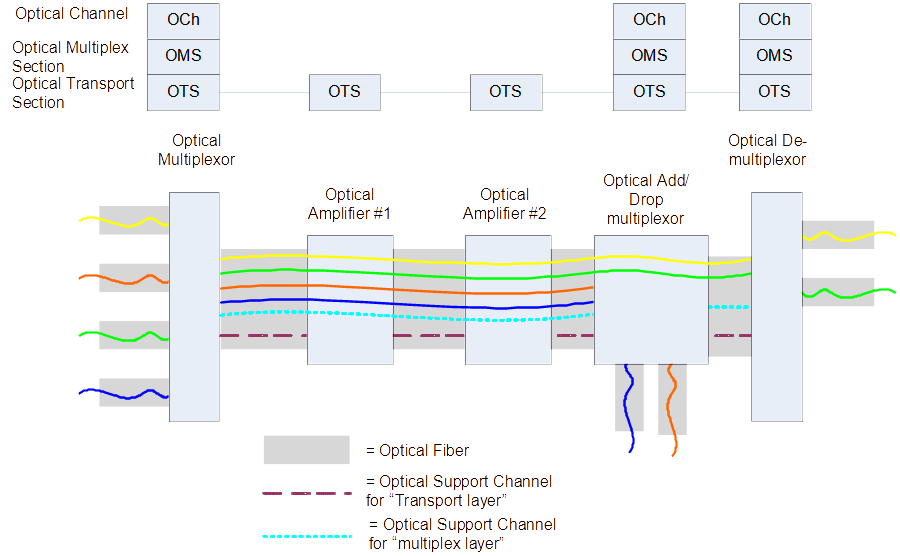
WDM Layers
The Three-Plane Network Model
In addition to decomposing networks by layer and geography there is the three plane view:
- Data Plane: This is where the user traffic flows in a network.
- Control PLane: controls the switching and multiplexing functions in the network. For IP networks this is performed by protocols such as OSPF, BGP, etc…
- Management Plane: Manages the networks
Control Plane Examples
- Ethernet: Learning bridge, spanning tree algorithm for loop prevention
- IP routing: OSPF, RIP, BGP
- MPLS: enhanced OSPF, RSVP-TE (signaling)
- WSON/GMPLS: enhanced OSPF, enhanced RSVP-TE
Network Management 1
FCAPS Summary
- Fault Management
- the detection, isolation and correction of abnormal operation of the telecommunication network and its environment. Also testing and trouble administration.
- Configuration Management
- functions to exercise control over, identify, collect data from and provide data to NEs. Includes: Network Planning and Engineering, Installation, Inventory, Service Planning and Negotiation, Provisioning.
Network Management 2
FCAPS Summary
- Accounting Management
- Usage monitoring, generation of call records, billing systems, …
- Performance Monitoring
- Evaluates and reports upon the behavior of equipment and the effectiveness of the network or network element, gathers and analyzes statistical data for the purpose of monitoring and correcting the behavior and effectiveness of the network, NEs or other equipment and to aid in planning, provisioning, maintenance and the measurement of QoS.
- Security Management
Security Implications
Availability Dangers!
Attacks on the control plane: BGP is particularly vulerable see for example Internet Governance: Routing Security
Attacks on the management plane: See recommendations from Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency. Adversary’s dream: infiltrate IT or Network management systems. Has this ever happened?
Wireless Physical Layers
Popular Wireless Technology
Low Speed Wireless Examples
WiFi References
WiFi Physical (2.4GHz)
From Wikipedia
By Rbeede, Liebeskind (original) - https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:NonOverlappingChannels2.4GHzWLAN-en.svg, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=27849387
WiFi Physical Channel Example

WiFi Management
From IEEE 802.11 Standard

Getting WiFi Access
- Access Point (AP) advertises SSID (Beacon Management Frame)
- Authentication (Authentication Management Frame)
- Association with AP (Association Management Frame)
Simple Sequence Diagram
From IEEE 802.11 Standard

Example Associated Stations

Wireless Security Issues
- Confidentiality: Anyone can listen to your transmissions!
- Integrity: Easy to insert transmissions (don’t have to plug in)! “Man in the Middle” attacks…
- Availability: Jamming (interference) happens all the time! But there are more attacks possible on availability.
Kali Linux Wireless Attack Tools
As of 01/20/2021, includes WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee
Airbase-ng, Aircrack-ng, Airdecap-ng and Airdecloak-ng, Aireplay-ng, airgraph-ng, Airmon-ng, Airodump-ng, airodump-ng-oui-updateAirolib-ng, Airserv-ng, Airtun-ng, Asleap, Besside-ng, Bluelog, BlueMaho, Bluepot, BlueRanger, Bluesnarfer, Bully, coWPAtty, crackleeapmd5pass, Easside-ng, Fern Wifi Cracker, FreeRADIUS-WPE, Ghost Phisher, GISKismet, Gqrxgr-scan, hostapd-wpe, ivstools, kalibrate-rtl, KillerBee, Kismet, makeivs-ng, mdk3, mfcuk mfoc, mfterm, Multimon-NG, Packetforge-ngPixieWPS, Pyrit, Reaver, redfang, RTLSDR Scanner, Spooftooph, Tkiptun-ng, Wesside-ng, Wifi Honey, wifiphisher, Wifitap, Wifite, wpaclean
WiFi Phisher 1
From WiFi Phisher documentation
From the victim’s perspective, the attack makes use in three phases:
Victim is being deauthenticated from her access point. Wifiphisher continuously jams all of the target access point’s wifi devices within range by forging Deauthenticate or Disassociate packets to disrupt existing associations.
Victim joins a rogue access point. Wifiphisher sniffs the area and copies the target access point’s settings. It then creates a rogue wireless access point that is modeled by the target. It also sets up a NAT/DHCP server and forwards the right ports. Consequently, because of the jamming, clients will eventually start connecting to the rogue access point. After this phase, the victim is MiTMed.
MiTMed = “Man in the middled”
WiFi Phisher 2
From WiFi Phisher documentation
Victim is being served a realistic specially-customized phishing page. Wifiphisher employs a minimal web server that responds to HTTP & HTTPS requests.
As soon as the victim requests a page from the Internet, wifiphisher will respond with a realistic fake page that asks for credentials or serves malwares. This page will be specifically crafted for the victim. For example, a router config-looking page will contain logos of the victim’s vendor. The tool supports community-built templates for different phishing scenarios.